Subject
- #Relational Data Modeling
- #Physical Data Modeling
- #Database
Created: 2024-04-09
Created: 2024-04-09 23:01
If logical data modeling was the process of creating ideal tables suitable for relational databases, physical data modeling involves creating those ideal tables into actual usable tables, and focuses on performance improvement and optimization, including efficient storage space planning, object partitioning design, and optimal index design.
The method of finding slow queries that cause bottlenecks during service operation varies depending on the type of DBMS, and you need to search using slow query as a keyword.
Cache
If the performance issue is not resolved with the above methods, a process called denormalization or inverse normalization is performed.
It involves surgically modifying the structure of the table.
Normalization is like sacrificing read performance for the convenience of write operations. When normalization is applied, queries need to be written to join the data from multiple split tables.
However, normalization does not necessarily degrade performance, so it is essential to properly identify and examine the problem before proceeding with denormalization.
The link below is a good article that discusses denormalization, which we will cover later.
First, it's important to understand that denormalization should be performed after normalization. A non-normalized table is not always ideal from the beginning.
Since this knowledge is not immediately necessary right now, I'm going to just note it for now.
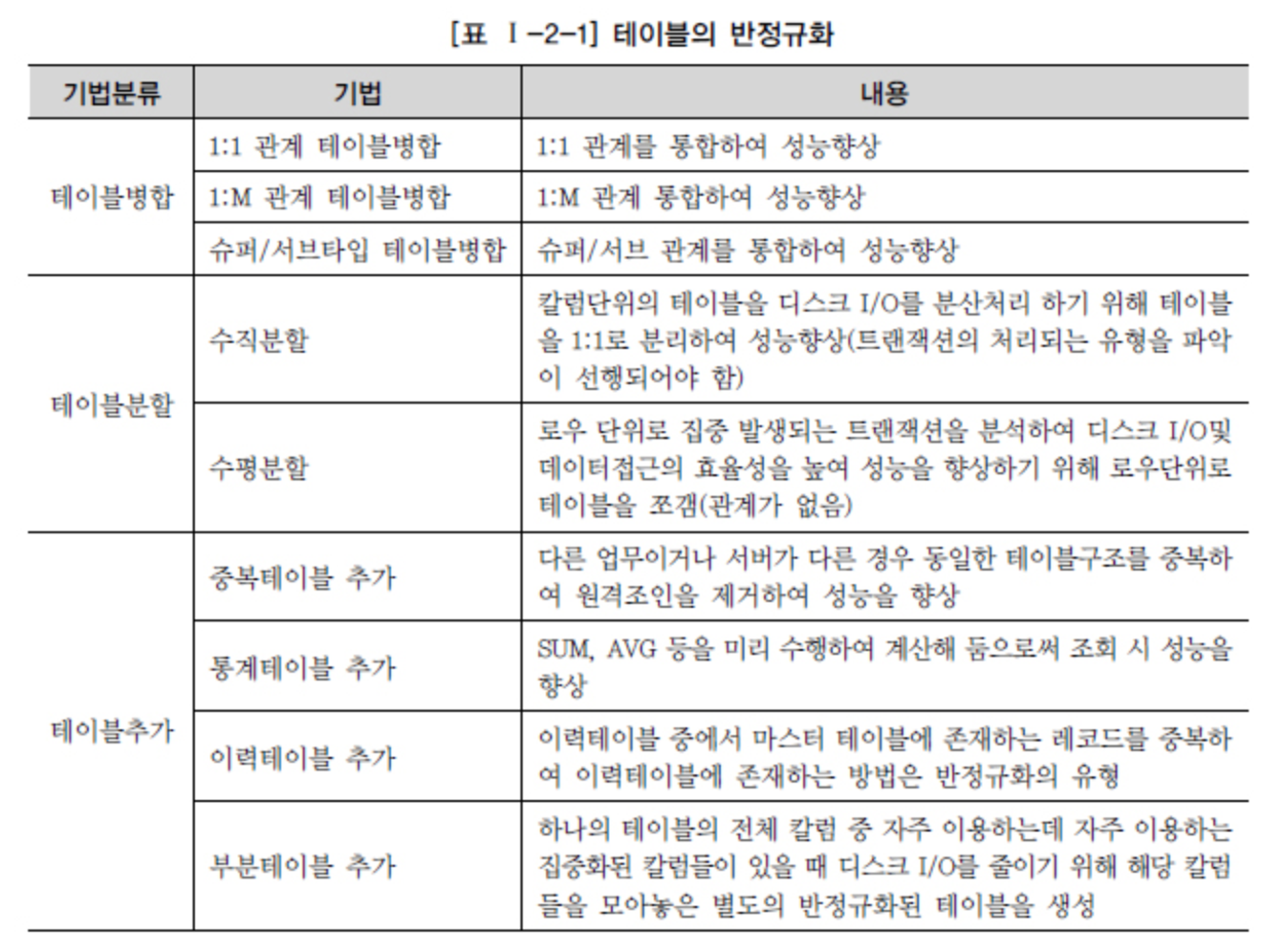
Source - DataOnAir - Denormalization and Performance
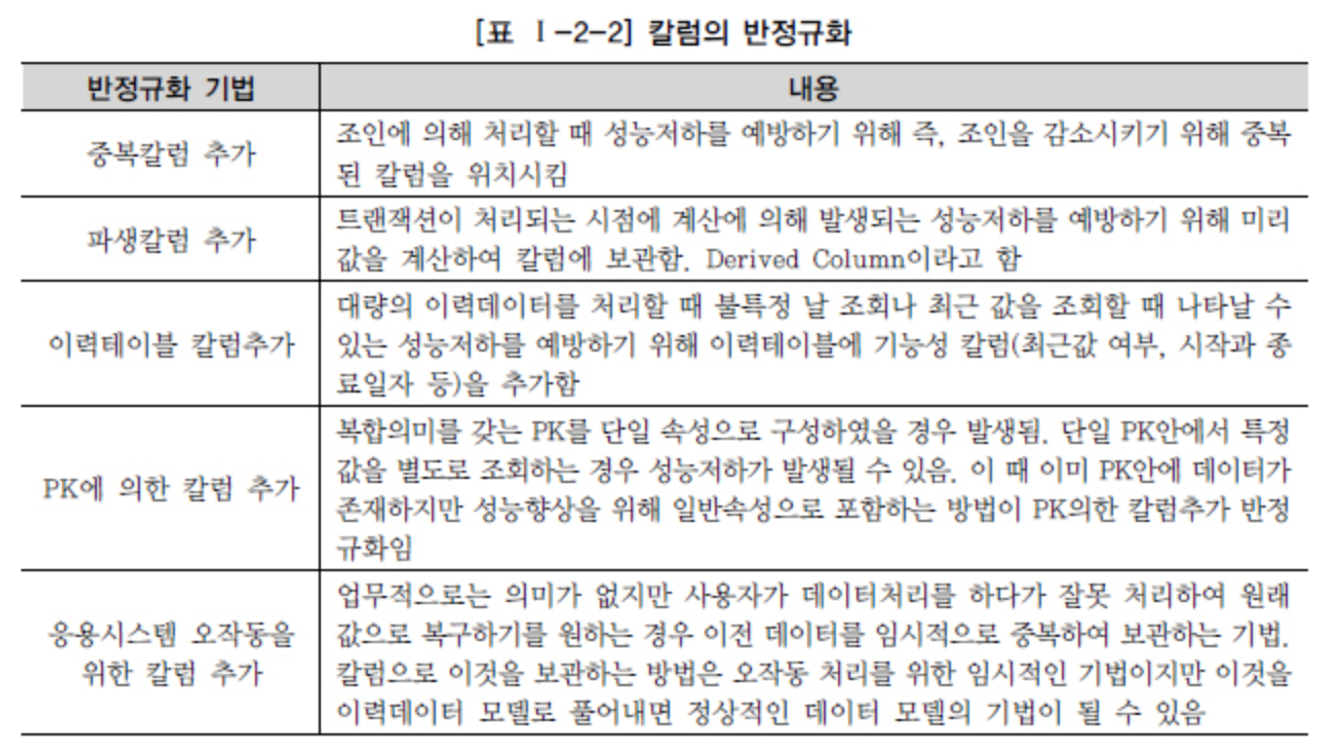
Source DataOnAir - Denormalization and Performance
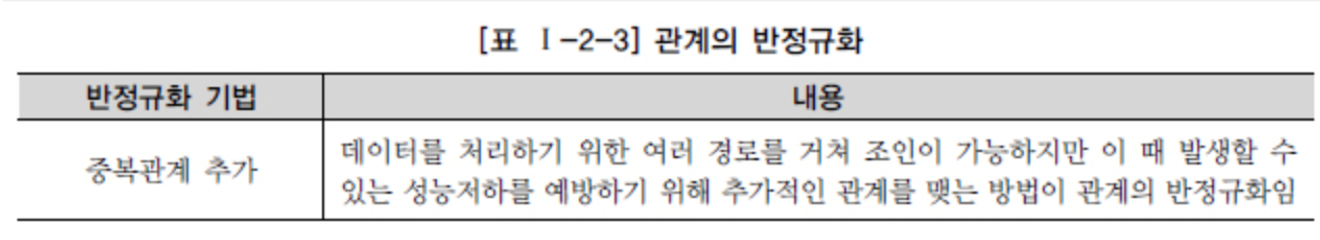
Source - DataOnAir - Denormalization and Performance
Comments0